
Header bidding has shaken up the digital advertising industry, with both advertisers and publishers hailing the method…
Table of Contents
on September 01, 2025
Adtech is much more than a simple trade between publishers and advertisers. If you are a part of the ad tech ecosystem, you know that an online advertising ecosystem is complex. It involves many parties, such as supply-side platforms(SSPs), demand-side platforms(DSPs), and ad marketplace. All of these complexities to achieve a single objective- displaying impactful online ads in less than a thousand milliseconds, flawlessly! In this massive digital advertising landscape, the ad server eventually does all the job behind the scenes. Most popular ad tech platforms, programmatically powered ad networks, and ad exchanges rely on these ad servers.
In this detailed guide, we will discuss what an ad server is, the types of ad servers, how ad serving works, and all the concepts related to ad server in detail.
Without further ado, let’s begin with understanding-
Ad servers are web-based technological systems that host, optimize, and distribute ad content across various apps, websites, and social media platforms. Such servers are also referred to as ad-tracking systems or campaign management platforms.
Ad servers can be considered as large containers of raw creative graphics. When users visit a web page or app, an ad creative is retrieved and served in the advertising slot. The new-age advanced ad servers also act as an interface with end-to-end ad management solutions. These let you set delivery parameters, target and monitor campaigns with advanced algorithms and analytics, and gather massive amounts of data.
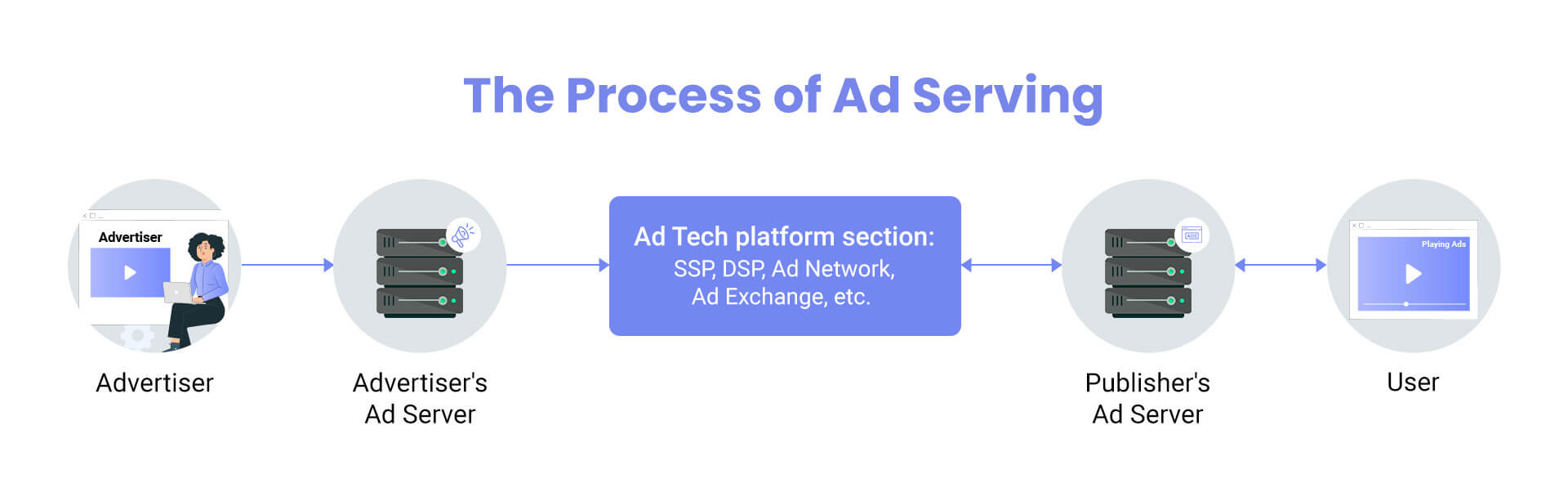
An ad-serving platform is the core element of every ad server. It is an ad tech process of delivering advertisements on various websites, apps, and social media platforms via ad tech software. In this process, the most relevant ads are selected for display using complex algorithms and advanced decision-making tools.
The ad selection process is strictly regulated by the guidelines established by advertisers and publishers, and the criteria set in the ad server itself. Such guidelines include settings for targeting criteria, digital ad formats, ad priority, ad placement, ad viewing frequency, earning potential, and more. Ad servers are also used for ad tracking, management, reporting, and billing.
The classification of video ad servers can be made according to the users and the relevant usages, such as:
Considering management and localization, video ad servers can be further classified into:
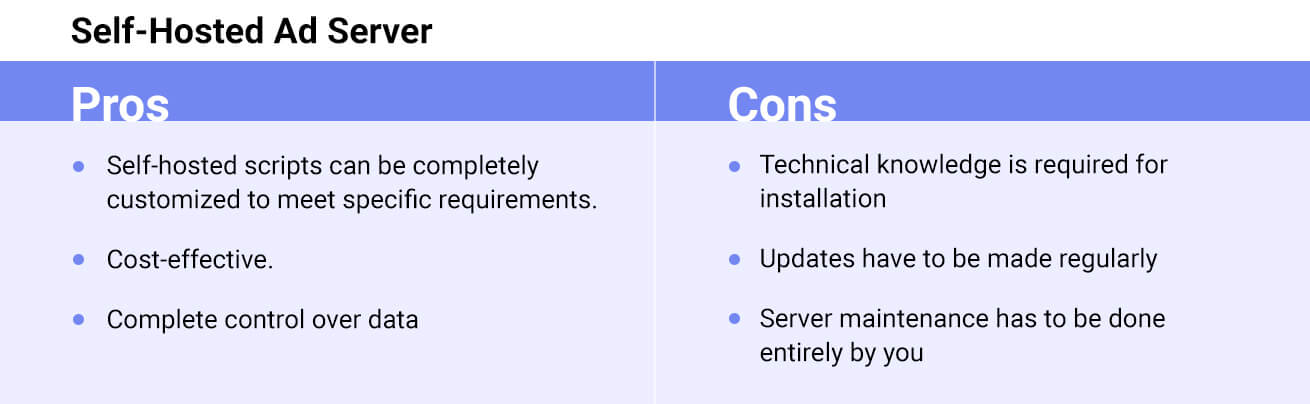
Self-hosted servers are installed and maintained by their owners. The main advantage of self-hosted ad servers is that the ad-serving technology is available for free or for a small one-time fee. However, it is the publisher’s responsibility to maintain and troubleshoot such servers. Since the scripts of self-served servers can be modified and customized at any time, they have broader functionalities.
Nonetheless, supporting stable and seamless functions requires considerable human resources, constant maintenance, and monitoring.
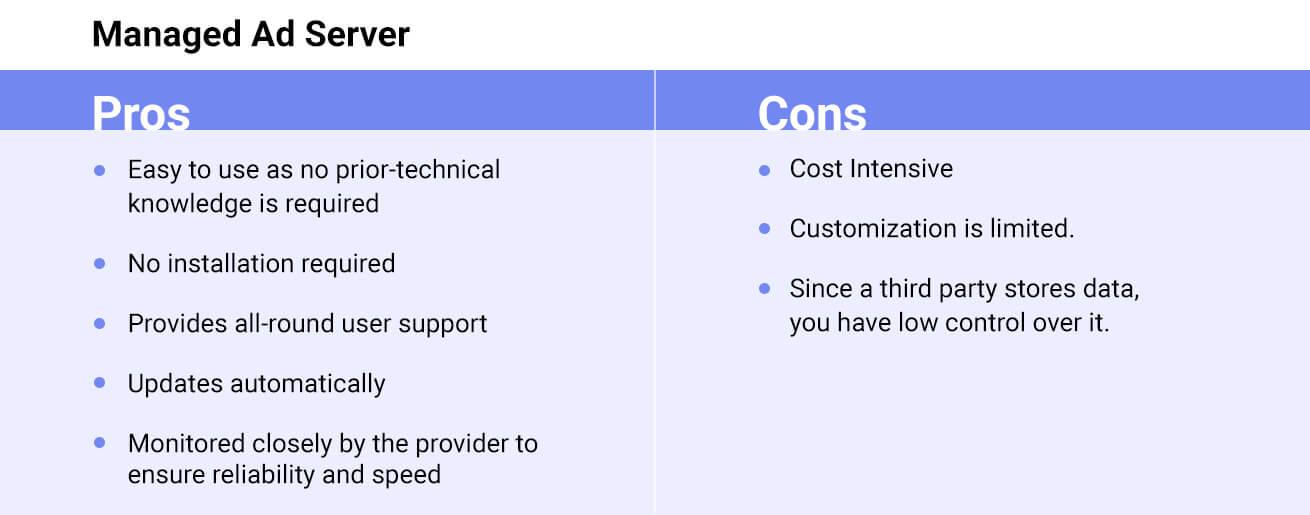
A managed video ad server is hosted by an ad-serving company or third-party vendors. Moreover, it does not require any special technical knowledge for operation. This is basically a SaaS technology that you “rent” by paying a monthly/yearly fee for access.
An ad server can be run either locally or remotely. You can have direct physical access to a local ad server if you have one. If not, you can consider using the capabilities of a third-party company that provides remote server access.
Publishers typically own local servers, whereas multiple publishers can leverage remote ad servers as they are managed and operated independently. In such scenarios, all ads are broadcasted from a single source, allowing advertisers to track their ad placement across the Internet.
In ad tech, the terms “demand-side platform” (DSP) and “supply-side platform” (SSP) is frequently used interchangeably with “ad server.” However, DSPs, SSPs, and ad servers are not the same things.
Nevertheless, DSPs and SSPs are frequently involved in the communication process between first and third-party servers. Consider a DSP to be an interface that allows you to manage an ad campaign across various ad servers. You can also consider supply-side platforms to be similar interfaces for publishers and their ad inventory.
Let’s now distinctively understand DSPs and SSPs!
DSP, or “Demand-Side Platform,” is an ad tech tool used by advertisers in marketing and advertising. It acts as an interface that connects advertisers with the programmatic advertising ecosystem. It also helps them manage purchasing advertising media from the ecosystem.
SSP or “Supply Side Platform” or “Sell Side Platform” refers to an ad tech tool used by publishers in marketing and advertising. It connects publishers to the programmatic advertising ecosystem and manages how they sell their ad inventory through that ecosystem.
As we discussed earlier, ad servers store ad creatives, serve selected ads automatically to visitors as per defined rules, and collect user interaction data such as impressions and clicks.
The capabilities of a video ad server remain the same regardless of who uses it. While publishers use them for managing ad inventories and reporting, advertisers generally use these servers to manage ad campaign creatives.
Overall, usage of ad servers by both parties involves an advertising transaction wherein publishers sell available ad inventory to the advertiser directly, by complying to a mutually defined set of terms and conditions.
While such a direct deal is established, the publisher’s (first-party) ad server directly interacts with the advertiser’s (third-party) ad server to deliver advertiser’s ads to users visiting the publisher’s website.
Despite having similar capabilities, publisher’s and advertiser’s ad servers have different functions.
Now let’s dive deeper into how these servers work individually.
These servers, also known as “first-party ad servers,” help media sellers enhance the value of every impression. They optimize yield by serving the highest-paying advertisements to viewers across their personal domain. Publishers use such servers to determine the most relevant viewers for each impression. They also track how users interact with ads (whether they click or skip them), evaluate the ad display frequency, and monitor overall performance.
Publishers also use sell-side first-party ad servers to display ad creatives with varying technical and targeting requirements across multiple formats. The ad-serving interface enables digital media sellers to add new ad buyers to their contact lists easily. It also lets sellers edit, manage, and delete partners efficiently.
Publishers can also collect independent reports on ad creatives, explore the best-performing ad formats, and optimize their ad space over time.
These servers, also called “third-party ad servers,” help advertisers save time and costs by storing and managing the ad code. Marketers are only required to download ad units to third-party ad servers once. They can modify the downloaded units anytime without sending the updated copies to each trading partner.
Alternatively, the latest versions of the advertisers’ creatives assist advertisers in getting access using the HTML link tag, which eventually leads to the server. Top video ad servers even provide separate reports on performances, spending, and revenue of every ad to advertisers.
Third-party ad servers (buy-side) are built considering the media buyer’s logic. They help advertisers to maximize profits, reduce costs, and centralize the ad-buying process across publishers. Advertisers can also use these servers to track metrics like impressions, clicks, conversions, and purchases.
Step 1) Ad-serving technology is complex and involves multiple steps. It all begins with a user’s visit to an app or website. An IP connection is then established between the user’s computer and the publisher’s web server. As the website starts loading, ad tags on the site load and call the sell-side ad server.
Step 2) On receiving the ad request, publisher’s ad server immediately analyzes user data such as time of day, language, online behavior, geolocation, and demographic attributes (age, gender, employment, marital status, etc.). The data management platform can also transmit such information.
Step 3) The ad server then sends requests to ad exchanges, where buyers proceed to bid incase they are interested in the ad space and consider it relevant to the user.
Step 4) This server also analyzes the number of times the ad has been displayed to the specific user in the past. This is referred to as frequency capping. If the advertisement is displayed very frequently, it is rejected.
Step 5) A publisher ad server processes millions of buyer requests and selects the best-paying ad in milliseconds. It then redirects the browser to the marketer’s ad server, which retrieves the ad creative from the CDN (content delivery network).
Step 6) Finally, the advertisement is retrieved and downloaded successfully onto the web page, which is referred to as an impression. The user’s browser streamlines the entire online advertising process, right from ad selection and placement, regardless of the number of calls. This must take less than a second to ensure high viewability.
This was the fundamental concept of how ad servers organize the advertising process.
Now let’s understand how the ad serving process takes place on the publisher (first-party ad server) and advertiser(third-party ad server) sides.
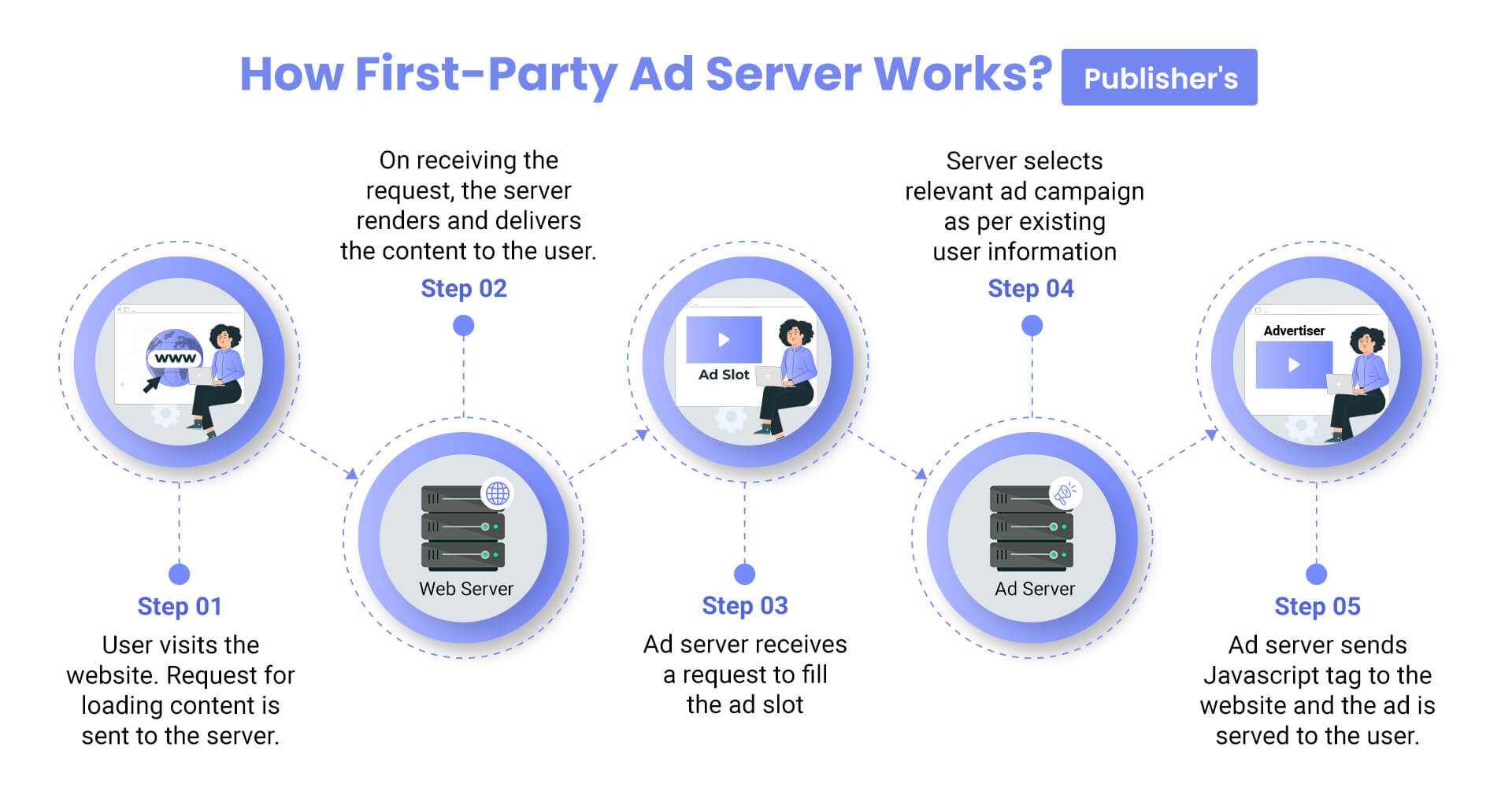
The process of managing ad calls is very simple in standalone first-party ad servers.
When the first-party ad server receives the ad call:
The ad creative is directly stored on the first-party ad servers in this configuration. However, even in direct deal arrangements, publishers do not commonly store advertisers’ creatives on their own video ad servers. Instead, third-party servers host the ad creatives that advertisers want to use.
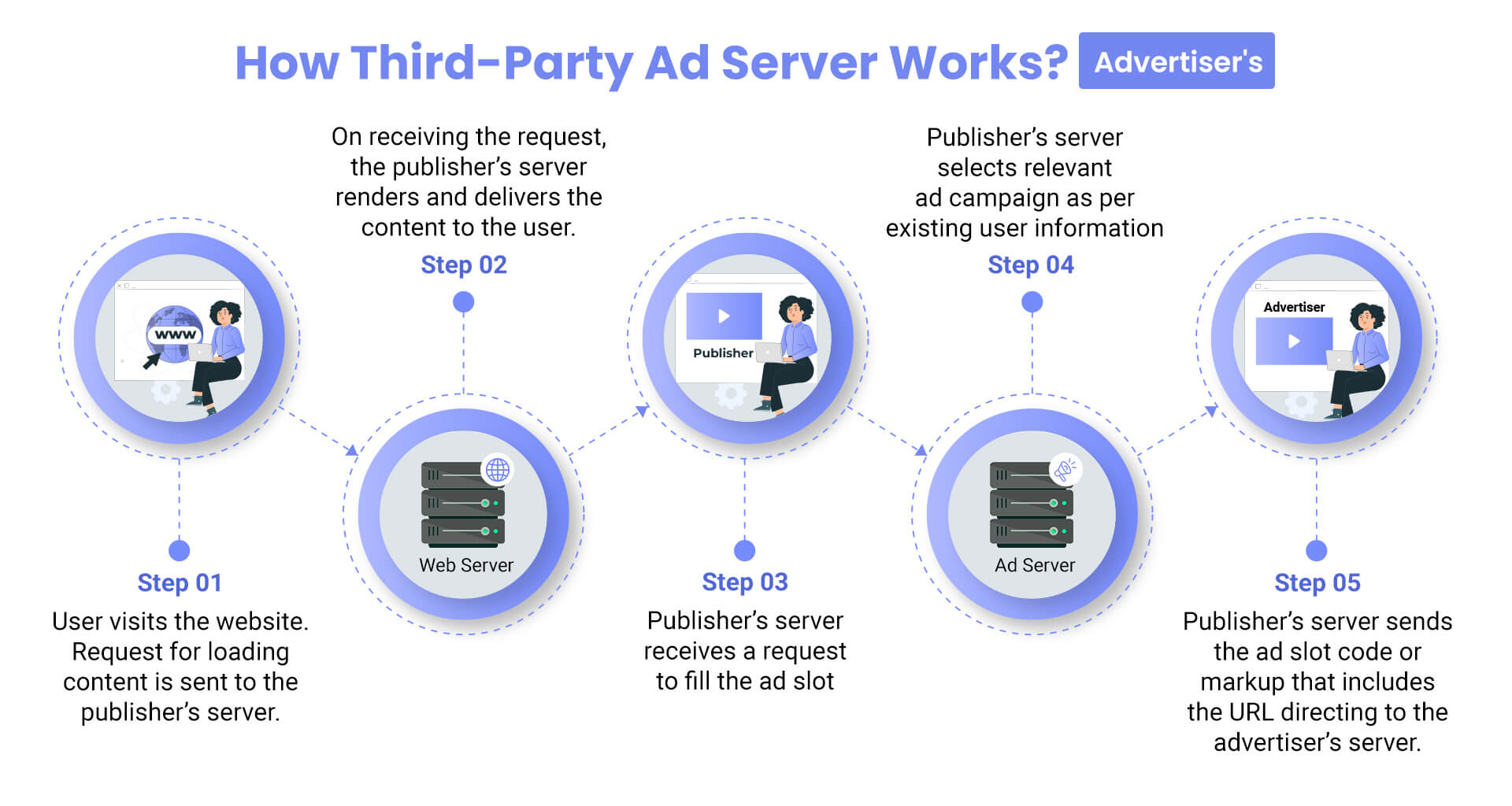
The process is similar to that of a standalone first-party ad server but with a few additional steps:
The process of ad serving work when SSPs and DSPs are involved is as follows:
This entire process is completed in milliseconds, usually before a page loads.
Most ad servers provide a combination of ad delivery and ad management features to advertisers, publishers, and ad networks. Others offer limited features. When selecting an ad server, ensure that it has the following features:
To begin, you must evaluate which tasks require the use of an ad server for your business. First and third-party servers are basically the same component of technology. However, different needs and challenges of the demand and supply sides make publishers and advertisers use them differently. Once your core tasks are defined, you can choose the ad-serving platform that performs such functions and caters to your overall business needs.
All ad servers can be technically classified as self-hosted and managed. Both of these definitely can be integrated and function together.
However, if the technology provider maintains a managed ad server, the configuration and maintenance of the self-hosted ad server are all on you.
A self-hosted ad server can be a cost-effective approach if you have a hands-on team with the right expertise in ad-serving technology. Alternatively, it is always recommended to choose a managed ad server as the technology providers always have skilled and experienced professionals who handle the end-to-end ad serving process.
An ad server must be highly efficient to grab users’ attention. Choose an ad server that can deliver inventory accurately and quickly with minimal disruptions. Regarding efficiency, processing power and versatility are also crucial factors.
Pick an ad server that will offer you a variety of ad formats to choose from and serve them across multiple platforms. These ads should also be customizable so that they can be adapted to different screen sizes.
Select a scalable ad server that can handle both change and growth while delivering ads. This will enable you to create high-quality ads, track their performance, and optimize them as needed.
Another essential factor to consider when choosing an ad server is the quality and diversity of its services. It has a significant impact on improving your ad campaign efficiency and overall ad performance. It must provide you with multiple high-quality ad formats and rich media elements, including banners, interstitials, video rolls, and carousels. It should also enable you to preview the ad format before making the selection.
A robust ad server also lets you experience cross-platform ad formats for desktops and mobiles, run targeted campaigns, and improve your online presence.
Choose an ad server with a transparent pricing structure for its services that will tell you precisely what you will pay without any hidden charges. You can also check if the server provides flexible plans to choose from based on your business needs and budget.
A good ad server solution provides you with the right technical support and 24×7 customer service. Being available to respond to queries and assist customers in the ad-building process can be a crucial differentiator in choosing the right platform for you.
With AI-powered optimization layer and next-gen features, Aniview’s Premium Ad Server enables publishers and advertisers to deliver multi-format video ads across web, mobile & CTV/OTT platforms seamlessly. Backed by next-gen features, Aniview’s Ad Player lets you easily manage inventory, demand channels, and ad delivery.
To explore more, Get a Free Demo!
Featured Posts

Header bidding has shaken up the digital advertising industry, with both advertisers and publishers hailing the method…

Video ads are becoming increasingly popular, and the mobile device app space is no exception. Find out what it takes to develop a video ad-friendly app.

Programmatic advertising is far from low-quality or ineffective. Aniview debunks some of the biggest myths about the platform. Read it here.

First time going to Dmexco? Feel like exploring the city? Here are our top places to visit!
Adding {{itemName}} to cart
Added {{itemName}} to cart